深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历(Depth-First Traversal)简称DFS。
算法思想:
- 首先以一个未被访问过的顶点作为起始顶点,沿当前顶点的边走到未访问过的顶点;
- 当没有未访问过的顶点时,则回到上一个顶点,继续试探别的顶点,直到所有的顶点都被访问过。
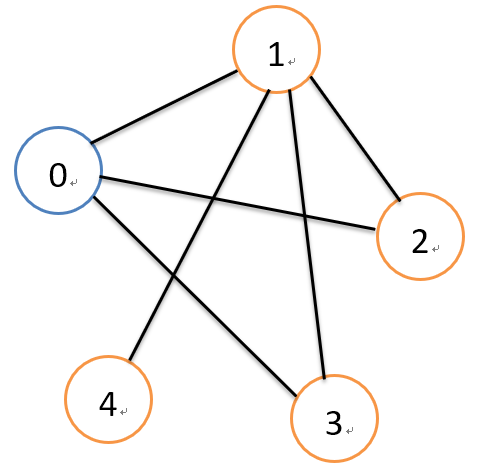
如上图,采用图的深度优先遍历的话,从0号节点遍历的顺序应该是:0,1,2,3,4.
程序源代码示例:
1 | public class DeepTravel { |
程序运行结果:
1 | 深度优先遍历的结果为: |
广度优先遍历
广度优先搜索算法(英语:Breadth-First-Search,缩写为BFS)。
其过程检验来说是对每一层节点依次访问,访问完一层进入下一层,而且每个节点只能访问一次。
程序示例:
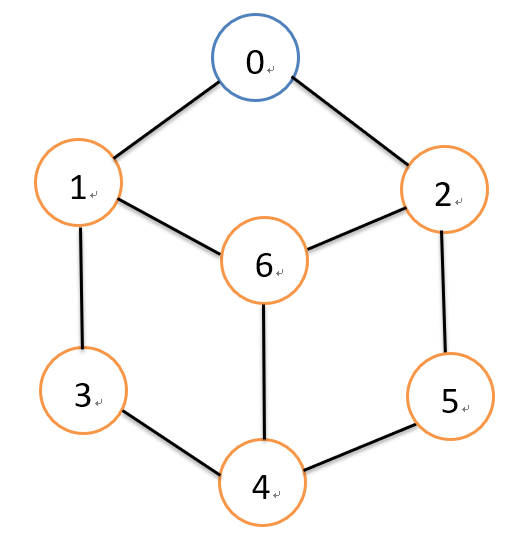
如上图,,采用图的广度优先遍历的话,从0号节点遍历的顺序应该是:0,1,2,3,6,5,4
程序源代码:
1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
程序运行结果:
1 | 广度优先遍历的结果: |
最短路径树
迪杰斯特拉算法简介
迪杰斯特拉算法是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有向图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
程序示例:
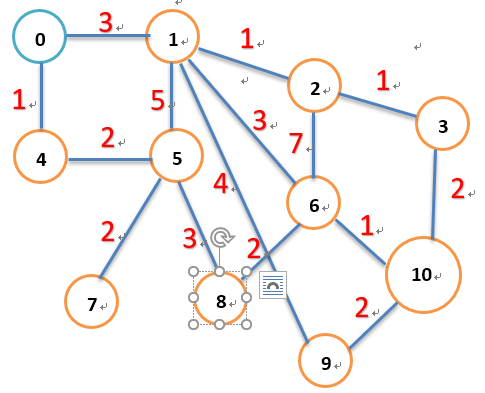
如上图,从求0号节点开始到所有节点的最短路径。
程序源代码:
1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
程序运行结果:
1 | {0=2, 1=3, 2=4, 3=5, 4=1, 5=3, 6=6, 7=5, 8=6, 9=7, 10=7} |

