Hive常用的HiveQL操作
Hive的基本数据类型:
Hive支持基本数据类型和复杂类型, 基本数据类型主要有数值类型(INT、FLOAT、DOUBLE ) 、布尔型和字符串, 复杂类型有三种:ARRAY、MAP 和 STRUCT。
a.基本数据类型
- TINYINT: 1个字节
- SMALLINT: 2个字节
- INT: 4个字节
- BIGINT: 8个字节
- BOOLEAN: TRUE/FALSE
- FLOAT: 4个字节,单精度浮点型
- DOUBLE: 8个字节,双精度浮点型STRING 字符串
b.复杂数据类型
- ARRAY: 有序字段
- MAP: 无序字段
- STRUCT: 一组命名的字段
常用的HiveQL操作命令:
创建、修改和删除数据库:
1 | create database if not exists hive; #创建数据库 |
注意,除 dbproperties属性外,数据库的元数据信息都是不可更改的,包括数据库名和数据库所在的目录位置,没有办法删除或重置数据库属性。
创建、修改和删除表:
1 | #创建内部表(管理表) |
视图和索引的创建、修改和删除:
主要语法如下:
1 | create view view_name as....; #创建视图 |
因为视图是只读的,所以 对于视图只允许改变元数据中的 tblproperties属性。
1 | #删除视图 |
里’org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.index.compact.CompactIndexHandler’是一个索引处理器,即一个实现了索引接口的Java类,另外Hive还有其他的索引实现。
1 | alter index index_name on table table_name partition(...) rebulid; #重建索引 |
如果使用 deferred rebuild,那么新索引成空白状态,任何时候可以进行第一次索引创建或重建。
1 | #显示索引 |
用户自定义函数:
在新建用户自定义函数(UDF)方法前,先了解一下Hive自带的那些函数。show functions; 命令会显示Hive中所有的函数名称:
1 | hive> show functions; |
若要查看具体函数使用方法可使用describe function 函数名:
例如:
1 | hive> describe function abs; |
首先编写自己的UDF前需要继承UDF类并实现evaluate()函数,或是继承GenericUDF类实现initialize()函数、evaluate()函数和getDisplayString()函数,还有其他的实现方法。
另外,如果用户想在Hive中使用该UDF需要将我们编写的Java代码进行编译,然后将编译后的UDF二进制类文件(.class文件)打包成一个JAR文件,然后在Hive会话中将这个JAR文件加入到类路径下,在通过create function语句定义好使用这个Java类的函数。
1 | #创建函数 |
数据操作:
主要实现的是将数据装载到表中(或是从表中导出),并进行相应查询操作,对熟悉SQL语言的用户应该不会陌生。
向表中装载数据:
这里我们以只有两个属性的简单表为例来介绍。首先创建表stu和course,stu有两个属性id与name,course有两个属性cid与sid。
1 | create table if not exists hive.stu(id int,name string) |
向表中装载数据有两种方法:从文件中导入和通过查询语句插入。
a.从文件中导入
假如这个表中的记录存储于文件stu.txt中,该文件的存储路径为/usr/local/hadoop/examples/stu.txt,内容如下。
stu.txt:
1 | 1 xiapi |
下面我们把这个文件中的数据装载到表stu中,操作如下:
1 | load data local inpath '/usr/local/hadoop/examples/stu.txt' overwrite into table stu; |
如果stu.txt文件存储在HDFS 上,则不需要 local 关键字。
b.通过查询语句插入
使用如下命令,创建stu1表,它和stu表属性相同,我们要把从stu表中查询得到的数据插入到stu1中:
1 | create table stu1 as select id,name from stu; |
上面是创建表,并直接向新表插入数据;若表已经存在,向表中插入数据需执行以下命令:
1 | insert overwrite table stu1 select id,name from stu where(条件); |
这里关键字overwrite的作用是替换掉表(或分区)中原有数据,换成into关键字,直接追加到原有内容后。
从表中导出数据:
a.可以简单拷贝文件或文件夹
命令如下:
1 | hadoop fs -cp source_path target_path; |
b.写入临时文件
命令如下:
1 | insert overwrite local directory '/usr/local/hadoop/tmp/stu' select id,name from stu; |
查询操作:
和SQL的查询完全一样,这里不再赘述。主要使用select…from…where…等语句,再结合关键字group by、having、like、rlike等操作。这里我们简单介绍一下SQL中没有的case…when…then…句式、join操作和子查询操作。
case…when…then…句式和if条件语句类似,用于处理单个列的查询结果,语句如下:
1 | select id,name, |
连接
连接(join)是将两个表中在共同数据项上相互匹配的那些行合并起来, HiveQL 的连接分为内连接、左向外连接、右向外连接、全外连接和半连接 5 种。
a. 内连接(等值连接)
内连接使用比较运算符根据每个表共有的列的值匹配两个表中的行。
首先,我们先把以下内容插入到course表中(自行完成)。
1 | 1 3 |
下面, 查询stu和course表中学号相同的所有行,命令如下:
1 | select stu.*, course.* from stu join course on(stu .id=course .sid); |
执行结果如下:
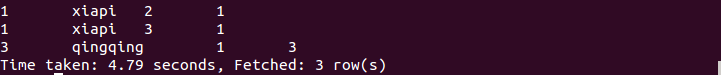
b. 左连接
左连接的结果集包括“LEFT OUTER”子句中指定的左表的所有行, 而不仅仅是连接列所匹配的行。如果左表的某行在右表中没有匹配行, 则在相关联的结果集中右表的所有选择列均为空值,命令如下:
1 | select stu.*, course.* from stu left outer join course on(stu .id=course .sid); |
执行结果如下:
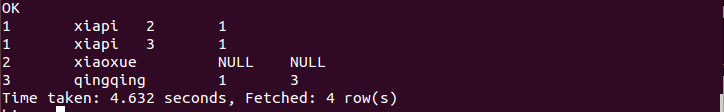
c. 右连接
右连接是左向外连接的反向连接,将返回右表的所有行。如果右表的某行在左表中没有匹配行,则将为左表返回空值。命令如下:
1 | select stu.*, course.* from stu right outer join course on(stu .id=course .sid); |
执行结果如下:
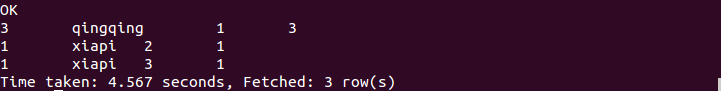
d. 全连接
全连接返回左表和右表中的所有行。当某行在另一表中没有匹配行时,则另一个表的选择列表包含空值。如果表之间有匹配行,则整个结果集包含基表的数据值。命令如下:
1 | select stu.*, course.* from stu full outer join course on(stu .id=course .sid); |
执行结果如下:
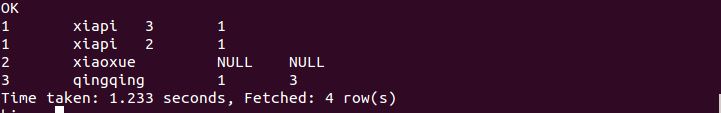
e. 半连接
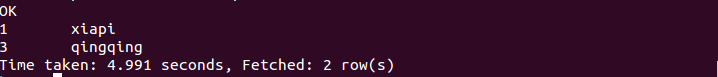
半连接是 Hive 所特有的, Hive 不支持 in 操作,但是拥有替代的方案; left semi join, 称为半连接, 需要注意的是连接的表不能在查询的列中,只能出现在 on 子句中。命令如下:
1 | select stu.* from stu left semi join course on(stu .id=course .sid); |
执行结果如下:
子查询
标准 SQL 的子查询支持嵌套的 select 子句,HiveQL 对子查询的支持很有限,只能在from 引导的子句中出现子查询。
注意,在定义或是操作表时,不要忘记指定所需数据库。
Hive简单编程实践
在MapReduce中要实现单词统计,需要一百多行代码;而在hive中只需要几行代码就可以,示例如下:
1 | create table docs(line string); |
这样就会把统计好的单词数放入到word_count表中。
由上可知,采用Hive实现最大的优势是,对于非程序员,不用学习编写Java MapReduce代码了,只需要用户学习使用HiveQL就可以了,而这对于有SQL基础的用户而言是非常容易的。

